On May 9, 2024, China’s State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) opened a public consultation on the revised Administrative Measures for Adopting International Standards. The deadline for submitting feedback is June 8, 2024.
Compared to the old version issued in 2001, which is currently in force, the revised Administrative Measures introduce a number of key changes, summarized below:
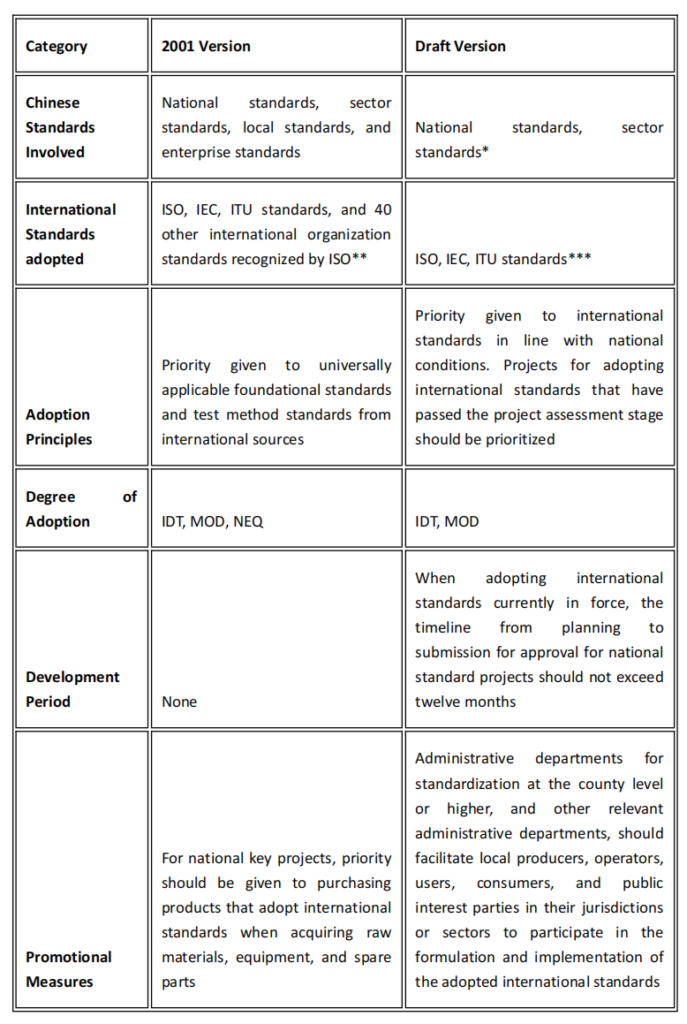
*Sector standards that need to adopt international standards will proceed according to the Administrative Measures for Sector Standards, which require compliance with the copyright policies of relevant international organizations, approved by the China member bodies of the international standards organizations.
**ISO no longer recognizes and publishes other standardization organizations.
***When there is a need to adopt an international standard, but these three international standards organizations have not developed any standards or the developed standards are not applicable, national standards can be formulated based on the standards published by other international and foreign organizations, following their intellectual property policies.
Additionally, the draft emphasizes compliance with the intellectual property policies of international standards organizations (stipulated in Articles 4, 11, 16, and 18 the principles, initiation, approval, and publication of national standard projects) proposes measures for the assessment and feedback of the adopted international standards.
The draft reflects China’s efforts to revise and refine the mechanisms and management models for adopting international standards to adapt to the current state of affairs and future goals of the standardization management system. It shows the ambition to further expand and accelerate the adoption of international standards. If, in the future, additional revisions can be made to strengthen measures to promote the implementation of international standards, this initiative would benefit even further. Moreover, the draft does not include other types of standards, reflecting China’s stance against encouraging the adoption of international standards by local, association, or enterprise standards.




