On April 9, 2025, The Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC) released a Question & Answer to address common questions regarding data export security management policies. This Q&A aims to help the data processors strengthen their understanding of the best compliance practices in cross-border data activities. The Q&A consists of three parts, and this is the part 3.
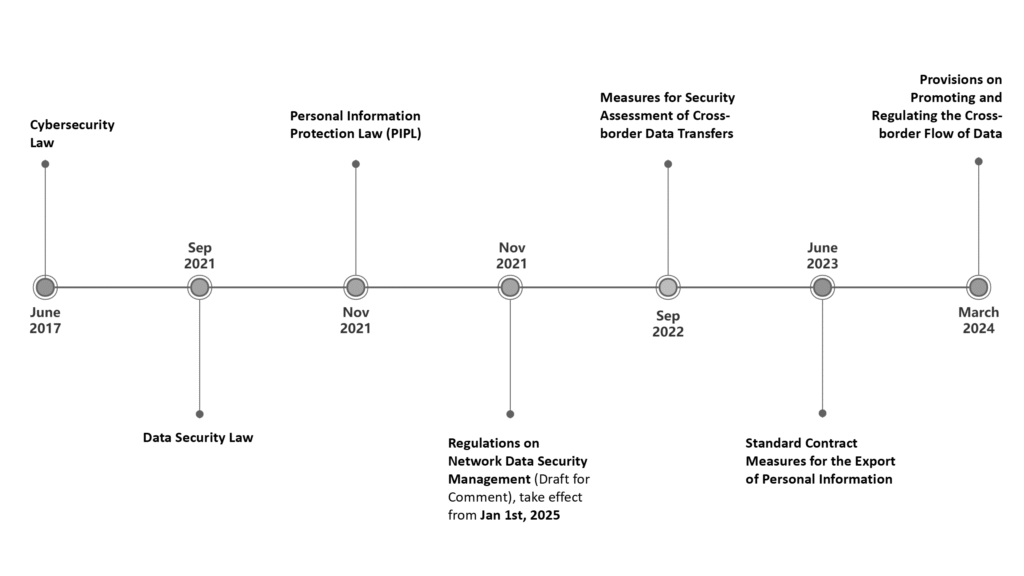
Before starting to read the Q&A, a list of China’s current laws and regulations regarding data security is provided below to help reader gain a structured overview of China’s current legal framework:
Question 7: How do foreign-invested enterprises play a role in the process of formulating industry technical standards?
Answer:
Guiding relevant professional institutions in the process of formulating sectoral technical standards, the CAC also highly values and actively encourages the participation of both Chinese and foreign enterprises, as well as other stakeholders. This ensures that the standard-setting process fully considers the needs of relevant domestic and international parties.
First, the participation mechanism is open and transparent. The CAC directs the National Cybersecurity Standardization Technical Committee to adhere to the principles of openness, cooperation, and broad participation. It publicly solicits members for working groups on an ongoing basis. Members of the committee and its sub-working groups include a number of representative foreign-invested enterprises. These enterprises enjoy equal rights and obligations as domestic companies and institutions in terms of participating in discussions and contributing to standard development. As members of the working group, foreign-invested enterprises can participate throughout the entire process and provide opinions and suggestions at all stages of standard development.
Second, the procedures for standard-setting are open and transparent. By publicly soliciting standard requirements and co-authoring organizations from society, and by seeking public comments on draft standards, fairness and impartiality are ensured for all relevant parties involved in the standard-setting process.
Question 8: Are those more convenient channels for cross-border personal information transfers within corporate groups?
Answer:
On the one hand, if multiple domestic subsidiaries belong to the same corporate group and their cross-border data transfer scenarios are similar, the parent company can act as the filing entity to consolidate and submit applications for data export security assessments or file standard contracts for personal information transfers abroad. This approach improves the efficiency of cross-border data workflows.
On the other hand, the CAC is promoting the introduction of relevant management measures for certification of personal information protection in cross-border transfers. These measures will guide third-party professional certification bodies to certify cross-border personal information transfer activities.
Once either the domestic enterprise or the overseas recipient passes the certification, the enterprise can conduct personal information transfers abroad within the scope of the certification. For multinational groups that have passed the certification, personal information transfers can be conducted within the group without the need to separately sign standard contracts for personal information transfers with subsidiaries in different countries.
Question 9: Is there a specific process for extending the validity period of data export security assessment results?
Answer:
The Regulation on Promoting and Regulating Cross-Border Data Flows extends the validity period of data export security assessment results from the original 2 years to 3 years. It also clarifies that if the validity period expires, and the data processor needs to continue conducting cross-border data activities without any circumstances requiring a re-application for a data export security assessment, the data processor may apply to extend the validity period of the assessment results within 60 working days before the expiration. The application is submitted through the provincial cyberspace administration department to the national cyberspace administration department.
Upon approval by the national cyberspace administration, the validity period of the assessment results can be extended for another 3 years. Currently, the CAC is actively soliciting opinions from all parties and expediting research on the process for extending the validity period of assessment results. It plans to clarify this process by revising and issuing relevant policy documents, thereby creating more favorable conditions for enterprises and institutions engaging in data export activities.
Access to Part 1 & 2
- Part 1: Part 1—Q&A on China’s Data Export Security Management Policies – sesec.eu
- Part 2: Part 2—Q&A on China’s Data Export Security Management Policies – sesec.eu
Access to the original Q&A in Chinese




