On February 12, 2025, the Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC) released the Administrative Measures for Compliance Audits on Personal Information Protection (hereinafter referred to as the Measures). These regulations will take effect on May 1, 2025.
China’s Personal Information Protection Law and the Regulations on Network Data Security Management require personal information processors to regularly conduct compliance audits on personal information protection. The Measures provide a detailed framework for implementing this requirement, specifying how compliance audits should be conducted, the selection of audit institutions, audit frequency, and the obligations of both personal information processors and professional auditing institutions. The goal is to establish a systematic, targeted, and practical regulatory framework to guide personal information processors in conducting compliance audits.
Key Provisions:
1. Scope and Frequency of Compliance Audits
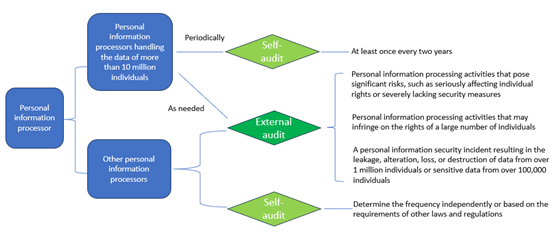
The Measures define two situations in which compliance audits must be conducted:
-
- Self-conducted audits: Personal information processors must conduct compliance audits either through an internal department or by engaging a professional institution to assess whether their personal information processing complies with relevant laws and regulations. Processors handling the personal information of over 10 million individuals must conduct audits at least once every two years.
- Regulatory-mandated audits: If the competent regulatory authority identifies high risks in personal information processing activities, potential harm to a large number of individuals, or a personal information security incident, it may require the processor to engage a professional institution to conduct a compliance audit.
2. Obligations of Personal Information Processors
-
- When conducting compliance audits as required by regulatory authorities, personal information processors must support the audit process, bear the audit costs, and complete the audit within a specified timeframe.
- They must submit the compliance audit report and rectify any identified issues in accordance with regulatory requirements.
3. Audit Guidelines
The Measures include an Annex: Guidelines for Compliance Audits on Personal Information Protection, which outlines key legal and regulatory requirements related to personal information protection. It provides a structured framework for conducting compliance audits and highlights critical areas of focus. Personal information processors conducting self-audits or regulatory-mandated audits must refer to these Guidelines.
4. Obligations of Professional Audit Institutions & Regulatory Oversight
The Measures specify the responsibilities of professional institutions conducting compliance audits. They also clarify the supervisory and enforcement responsibilities of regulatory authorities. Additionally, the Measures outline legal consequences for non-compliance by personal information processors and professional institutions.
Notably, the Measures do not provide detailed requirements for the compliance audit process. However, a national standard currently in development—Data security technology — Personal Information Protection Compliance Audit Requirements (currently at the draft for public consultation stage)—offers comprehensive guidance on the compliance audit process. This standard provides detailed references for various audit stages, including audit planning, preparation, execution, reporting, issue rectification, and archival management. As an important supplement to the Measures, this standard is expected to be finalized and released soon. European stakeholders are advised to closely follow its progress and provide feedback during the consultation process.
Reference: