On January 12, 2024, the Standardization Administration of China (SAC) issued the Guidelines on the Establishment of National Standard Projects in 2024 (referred to as the Guidelines). With ongoing standardization reforms, China is transitioning from a government-led development model to one driven by both government and market forces. To boost market actors’ involvement in standardization, China has raised the threshold for developing government-led standards (national compulsory and recommended standards) to reduce unnecessary market interference. The Guidelines clarify China’s stance on national standard development and lay the groundwork for future national standardization efforts.
The document includes five sections: general requirements, key areas for national standardization, project application requirements, relevant application materials, and contact information for national standards (samples) development or revision. Here are the key takeaways from the Guidelines:
- Institutional opening-up in standardization:
- Convergence with international standards: The Guidelines promote converting international standards into national ones and developing international and national standards simultaneously based on the same draft to align Chinese and international standards.
- Foreign-language translation of national standards: Besides convergence with international standards, the Guidelines emphasize translating national standards into foreign languages to promote Chinese standards globally. It requires translating all national compulsory standards not converted from international standards, in principle.
- Standardization areas: The Guidelines identify key areas for national standardization (reference materials) and detail SAC’s encouragement for national standard development in these areas.These key areas include consumption products, equipment manufacturing, materials, emerging technology, new-energy, energy conservation and pollution reduction, green and low carbon, agricultural and rural areas, modern service, safety and emergency, administrative management and social services, as well as national reference materials.
- Requirements for national compulsory standard development: The Guidelines stress that national compulsory standards should strictly focus on safety, public health, and environmental protection. These standards must be formulated based on a clear legal basis and implemented under governmental authority surveillance to handle non-compliance cases based on relevant legislation.
- The significance of a standardized system. Among the application materials is a comprehensive standard system table, outlining the blueprint for standardization in the forthcoming years. It is strongly advised for international stakeholders to closely monitor the standards system within pertinent industries as outlined by governmental authorities. These insights can offer valuable foresight into forthcoming national standards.
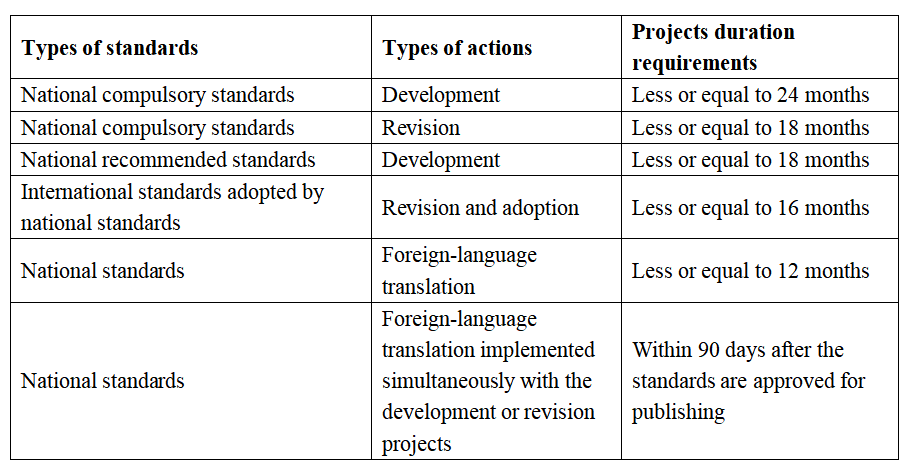
- Specific time constraints allocated to various types of standard projects (as indicated in the table below). Additionally, expedited procedures, known as fast-track procedures, are permissible for the standardization of emerging technologies or urgently demanded new products with significant market consumption potential.
- Access to governmental authorities.The Guidelines provide contact details including names, email addresses, postal addresses, and office phone numbers of relevant individuals. Stakeholders are encouraged to engage with them for inquiries regarding national standard projects, sample projects, or translations of national standards into foreign languages.
In summary, the Guidelines serve as a crucial point of reference for stakeholders involved in drafting national standards or monitoring industry trends. Moreover, they underscore the pivotal role of the standards system in guiding the formulation and revision of national standards in the immediate future. Ultimately, efforts towards institutional openness in national standards are anticipated to foster alignment with international community regulations.




