On January 8, 2024, China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology released the Guidelines for the Construction of the National Automotive Chip Standardization System (hereinafter referred to as the Guidelines). The Guidelines are the result of the collective efforts of over 200 experts from more than 60 enterprises, research institutes and universities, absorbing opinions from various segments of the industry. The goal set by the Guidelines is to develop more than 30 automotive chip standards of importance by 2025, meeting the basic requirements for product security, reliable application and pilot trials; the target increases to over 70 standards by 2030.
Background
Automotive chips, as the core components of vehicles’ electric systems, are essential for the transformation and upgrading of the automotive industry. Yet, the application scenario of automotive chips make them significantly different from other types of chips, as they have higher requirements in terms of adaptation to the environment, reliability, and security. On the other hand, according to ICwise (a provider of market research and advisory services specializing on the semiconductor and electronics industry), China has set clear goals for substituting the major types of automotive chips with domestically-made chips, within three years. For instance, for the automotive industry, over 50% of computing chips installed onboard must be produced domestically by 2025; overall, the substitution rate for different types of chips range from 40% to 55%.
Importance of standards system
During an interview with Chinese media, Mr. Yuan Chengyin, the General Manager of the National New Energy Vehicle Technology Innovation Center and Secretary General of the China Automotive Chip Industry Innovation Strategic Alliance (i.e., the main organization supporting the drafting of the Guidelines), indicated that “the introduction of the standard system provides reference for the application of independently developed chips installed onboard. This does not only helping China’s automotive chip industry to define the basic framework, but also the relevant enterprises to reduce costs and increase efficiency. In the past, the absence of a standards system for automotive chips meant that reference could be made only to foreign standards. In practice, this means that Chinese enterprises might be compliant with standards which may be out of date, or even not necessarily the most suitable for China’s application scenarios”.
The Guidelines aim to guide the development of standards in China, potentially impacting international standard development in the future. The secretariat of SAC/TC 114/SC34 has confirmed that the standards for automotive chips will not mandate the use of domestically produced chips. However, some stakeholders firmly believe that the Guidelines are aimed at promoting the independent development of automotive chips in China. This stems from the idea that enterprises along the supply chain may adjust their practices based on domestically developed standards, which could in turn pose challenges for foreign chips to enter the Chinese market at lower prices or relying on international standards.
Modifications
The Guidelines were revised after a previous draft for comments was released in March 2023. Apart from editorial changes and adjustments made in the body text, the final version:
- Removes the requirement for establishing a co-working group for automotive chips involving several relevant national technical committees;
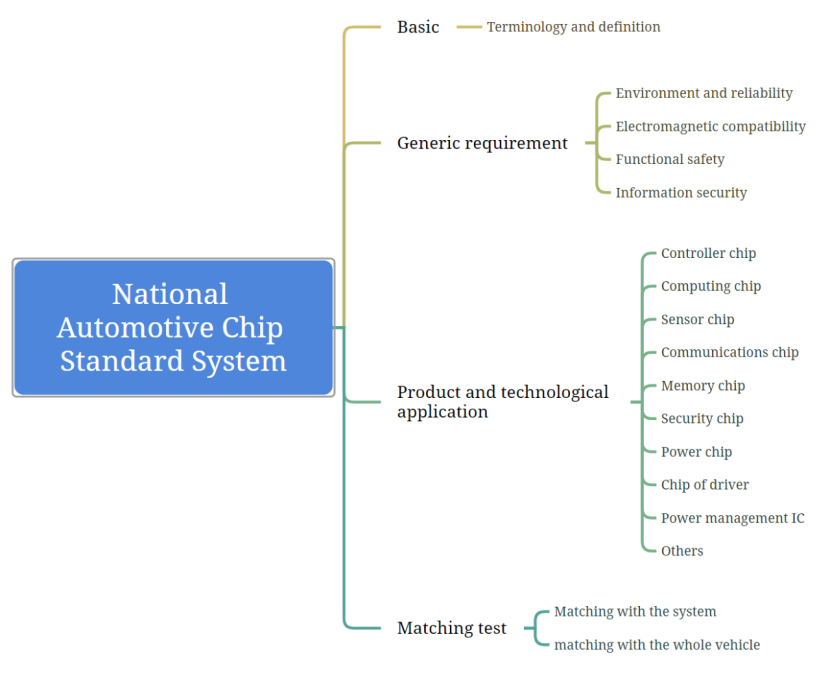
- Removes the standard list attached in the end, which might be due to the fact that the majority of the standards previously indicated arestill at a very preliminary stage of development.
Technical committees involved
The Guidelines reiterate the importance of deepening international exchanges and cooperation in UN/WP.29 as well as ISO and IEC. In addition, as the previous list of standards attached was removed, foreign stakeholders are recommended to closely track the dynamics of three specific technical committees, namely TC599 on Integrated Circuits, TC114 on Road Vehicle, and TC78 on Semiconductor Devices. These are expected to be the main platforms for the development of automotive chips standards. At the same time, technical committees on communication, information technology and Beidou Satellite Navigation will also be involved.
The China Automotive Technology and Research Center, which hosts the secretariat of TC 114, has established the Automotive Chips Standard Researching Group, thanks to joint efforts with other TCs such as TC114/SC15 on Electrical Equipment, TC114/SC27 on Electric Vehicles, TC114/SC29 on Automotive Electronics EMC, and TC114/SC34 on Intelligent and Connected Vehicle. In 2022, three standard drafting groups were established, each focusing on specific standardization topics. At the governmental level, a joint working group has been established by officials from MIIT’s Manufacturing Industry No. 1 Bureau, the Department of Science and Technology, and the Department of Electronic Information.
In conclusion, the Guidelines reflect China’s efforts to developing its own automotive chips, with the aim to support the development of domestic industries and gradually replace foreign supplies. Relevant technical committees and working groups have been established for this purpose. Therefore, foreign stakeholders are strongly recommended to keep tracking the dynamics of their activities, as well as the alignment or differences between China’s standards and international ones.
Figure 1. National Automotive Chip Standard System