On 18 April 2023, China’s National Information Security Standardization Technical Committee (TC260) released the Cybersecurity Standard Practice Guide — Guidelines for the Implementation of Cyber-data Security Risk Assessment (Draft for Comment) (hereinafter referred to the Guidelines).
According to TC260’s analysis of Data Security Law (Article 22 and Article 30), the data security assessment system is one of the four data security systems to be established in China. From the perspective of standards the establishment of the data security assessment system involves the development of standards aimed at clarifying the methods, processes, compilation of assessment reports for data security risk assessment, while developing detailed relevant requirements for data security assessment institutions and personnel management, qualification assessment, technical proficiency, etc. In general, the ultimate goal is to address standardization needs that are specified in Data Security Law. Therefore, the Guidelines were developed by TC260 to facilitate data security assessment and to provide guidance and instructions to the competent authorities and individual enterprises carrying out the risk assessment.
The Guidelines do not constitute a national standard, rather a type of standard-related technical document, aimed at publicizing cybersecurity related standards and knowledge, and providing practical guidelines for standard implementation. Still, there may be the possibility in the future that the Guidelines are transformed into a national standard or cited by certification rules – as it has previously been the case for the Cybersecurity Standard Practice Guide — Security Certification Rules for Personal Information Cross-border Processing.
It is expected that the cyber-data security risk assessment will highlight the role of prevention, and combine proactive identification of risks with responsive actions. The main targets of the risk assessment will be data protection measures and data processing activities implemented by relevant enterprises. The benefit of the risk assessment is that it enables data processors or the competent authorities to master the general situation of data security, identify potential loopholes, and outline suggestions s to enhance relevant capacity against attacks, destruction, theft, disclosure, and abuse of data.
To this end, the Guidelines:
- Lay outthe logic, processes and methods of cyber-data security risk assessment (see as follows Figure 1 and 2)
- Define the procedures and work content of cyber-datasecurity risk assessment
- Identify and evaluate security risks based on data security management, data processing activities, data security technology, personal information protection, and other aspects.
Figure 1. The logic of cyber-data security assessment
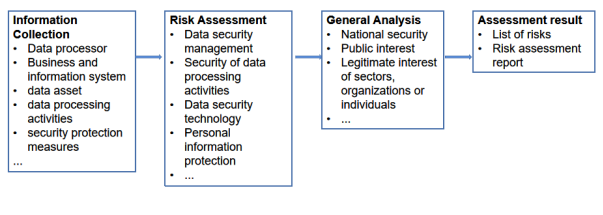
Figure 2. The assessment items for cyber-data security
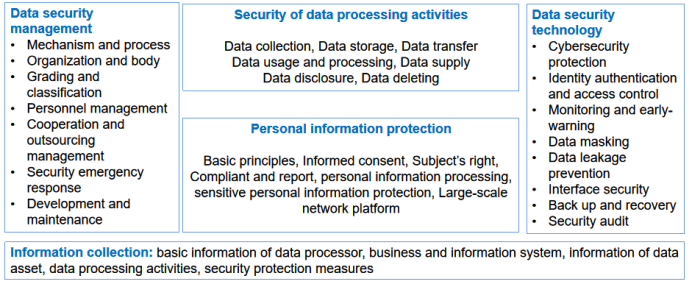
Foreign stakeholders should pay attention to their relation with the risk assessment required by certain data or personal information cross-border data transfer rules. The cross-border data transfer rules include the Measures for Security Assessment of Data Outbound Transfer, the Implementation Rules for Personal Information Protection Certification, and the Measures for the Standard Contract for Outbound Transfer of Personal Information. Of particular relevancy, the Guidelines clarify that, if their data activities fall under the scope of the above rules, relevant assessment shall be completed accordingly. In addition, the assessment for ensuring the security of cross-border data transfer focuses on:
- Whether the scenario for data outbound sorting is reasonable and complete, and whether it covers all business scenarios and product categories;
- Whether the outbound route is reasonable and complete, and whether it covers outbound transfer via a public network or private line;
- For transfers via public networks, the assessment shall monitor and verify whether the actual cross-border data transfer is consistent with the declared content.




