On 28 December 2021, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), together with seven other ministries, issued the 14th Five-Year Plan for the Development of Intelligent Manufacturing (hereinafter, referred to as the “Plan”). The Plan will guide the development of intelligent manufacturing (IM) industry through the next five years (the 14th five-year period).
The Plan first sets the quantitative objectives to be achieved for the IM industry in 2025, specifically:
- Transformation of the manufacturing sector: more than 70% large-scale manufacturing enterprises shall be digitalized, and 500 demonstration IM factories established.
- Supply of IM technologies and equipment: supplies of IM equipment and software shall satisfy 70% and 50% of market demand, respectively, and 150 IM solution providers shall be fostered.
- Strengthening the foundations for industry development: an IM standards system shall be established, with 200+ national and sector standards developed/revised. IM network infrastructure shall be set up, of which 120+ influential industrial internet platforms shall be established.
To achieve these objectives, the Plan outlines four key tasks:
- Facilitate innovation. The Plan identifies four product technologies and four system integration technologies as breakthrough points, and encourages leading enterprises, universities and research institutes to build up innovation incubators and test and verification platforms, in order to facilitate innovations as well as their transformation.
- Promote application. The Plan proposes to build up IM demonstration factories, implement the SME digitalization promotion project, and develop roadmaps to guide IM implementation in sectors of equipment manufacturing, electronics, raw materials, and customer products.
- Strengthen self-sufficiency. The Plan highlights the development of four kinds of IM equipment and six kinds of industrial software, with the aim to ensure the autonomy of China’s IM industry chain.
- Reinforce the foundations. The Plan stresses the importance of standardization, infrastructure construction, and cyber and data security in supporting the development of IM industry.
By now, China has planned 442 standards for its IM standards system, of which 281 have been completed, 108 are being developed, and 53 yet to be initiated – according to the Guidelines for the Construction of the National Intelligent Manufacturing Standard System (2021) (hereinafter, referred to as the “Guidelines”) issued in November 2021. The degree of completion of every branch of the system are illustrated in the figure below.
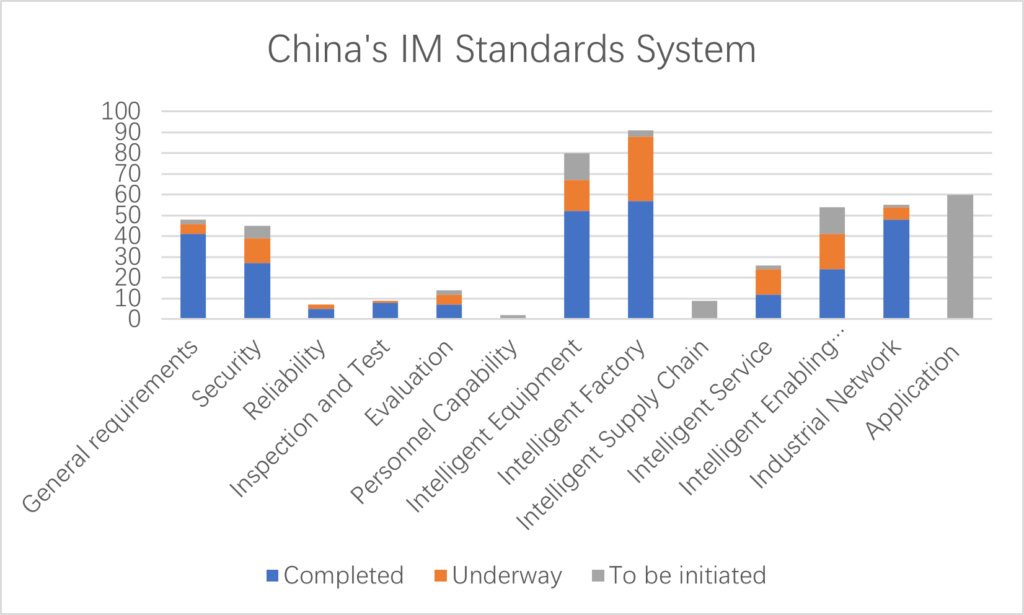
It can be seen that there is a huge gap in application standards, hampering the implementation of the IM standards system in actual production.
Therefore, the Plan proposes to establish the application standards systems for the sectors of textile, petrochemicals, building materials, automobile, aerospace, shipbuilding, power equipment, urban rail transport, household appliance, food, steel, nonferrous metals, and new energy. It also requires “(relevant SDOs) to accelerate the development of industry application standards”, and while “(the state) shall carry out pilot implementation of IM standards, form a standards group where national standards, sector standards, and association standards complement and coordinate with each other, and promote the application of the pilot achievements among SMEs and enterprises in the same industry”. All these statements indicate that the focus of IM standardization will turn to industry application in the next five year, and more sector and association standards may be included into the current standards system that is dominated by national standards, to support their implementation in various application scenarios.




