On November 15, 2024, China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), in collaboration with several other competent authorities, officially released the Guidelines on the Comprehensive Construction of the Standards System for the Lithium-ion Battery Industry (hereinafter referred to as the Guideline).
Purpose and Key Objectives
The Guideline aims to strengthen the standardization framework for the lithium-ion battery industry, outlining the key objectives, system structure, and organizational measures to support its implementation. A draft of the Guideline was initially issued by the MIIT in December 2023 to solicit public comments. The final version has been further streamlined, with more clearly defined objectives. The primary goals outlined in the Guideline include:
- By 2026, over 100 new national and sector standards will be developed, creating a more robust standards system to guide the high-quality development of the lithium-ion battery sector. The standardization efforts will continue to solidify China’s dominant position in the industry.
- Over 1,000 enterprises are expected to implement and promote these standards, while fostering innovation in standard service enterprises.
- China aims to participate in the creation of more than 10 international standards, further enhancing the global influence of its lithium battery standards.
Standard System Structure
The Guideline introduces a comprehensive standard system, which is categorized into six key areas (please refer to the figure below).
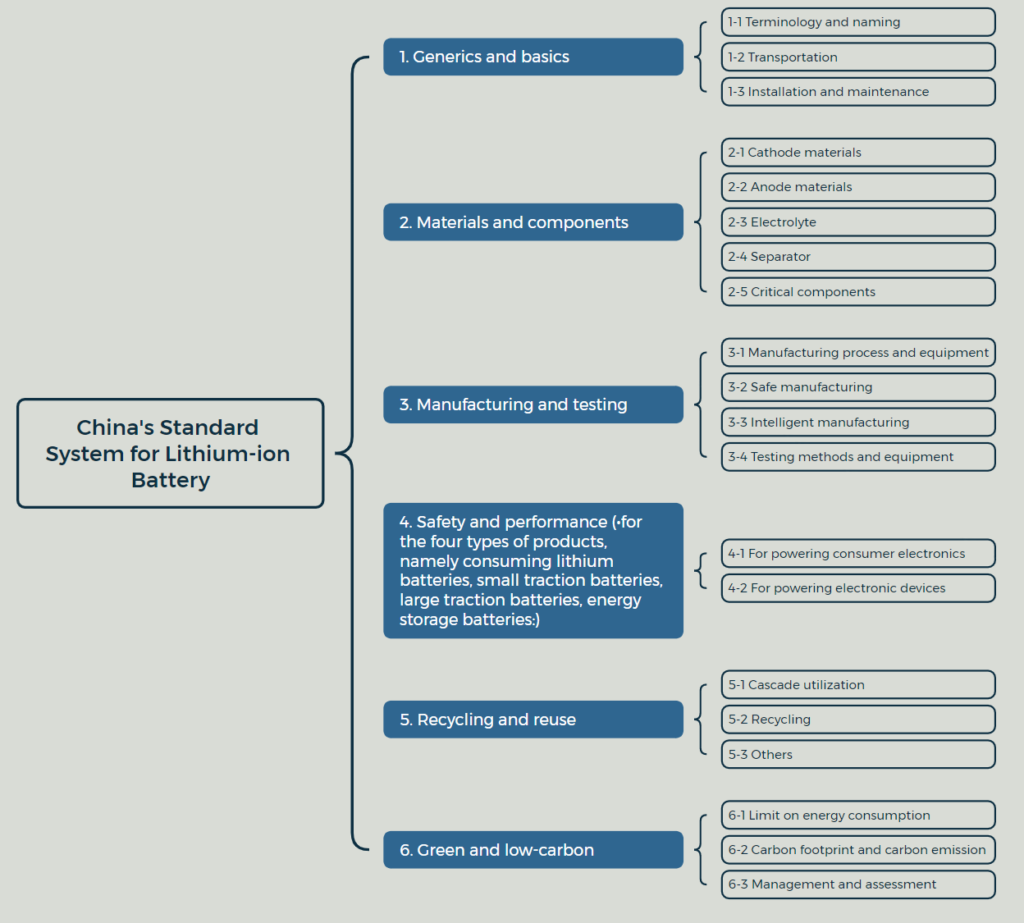
Organizational Support and Workforce Development
To ensure the success of the lithium battery standardization initiative, the Guideline emphasizes the optimization of organizational structures at all stages of the standardization process. Key actions include:
- Enhancing organizational capabilities among research institutions, manufacturers, and academic entities.
- Building a skilled workforce and cultivating talent in the standardization field.
- Strengthening the promotion and training on key standards, and guiding enterprises to align with the required standards.
This revised version maintains clarity and a formal tone while improving the overall flow and precision of the original content. Foreign stakeholders are advised to monitor the process of the follow-up actions and participate in the standardization if possible, as the standards might create impacts on the trade and market access.




