China joined the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in 1920. Currently, China ranks 2nd in ITU participation after the United States (Figure 1). Zhao Houlin, has served as ITU Secretary-General since 2015 (two consecutive terms: 2015-2018 and 2019-2022); before that, he had served as ITU Deputy Secretary-General for eight years; he also served two elected terms as Director of ITU’s Telecommunication Standardization Bureau (TSB).
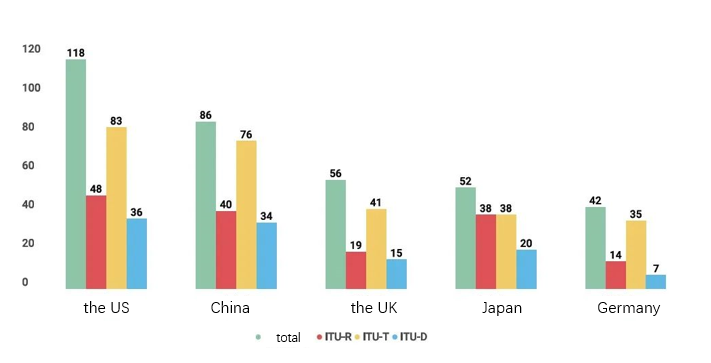
Figure.1 Top 5 countries with the largest number of ITU members (as of October 2021)
Participation in ITU
1. Participation as ITU-T SG chairman and vice-chairman
ITU-T currently has a total of 11 SGs. Among these, China holds the chairmanship of two SGs (Huawei and the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology); Japan also holds 2 chairmanships (CAICT and KDDI); while the chairpersons of the remaining 7 SGs are from Ghana, South Korea, Russia, Switzerland, United Arab Emirates, United Kingdom and United States.
In terms of ITU-T SG Vice-Chairman position, China ranks first (10 positions), followed by South Korea (8), Argentina (7), Tunisia (7) and Japan (6). See Figure 2 for more details.
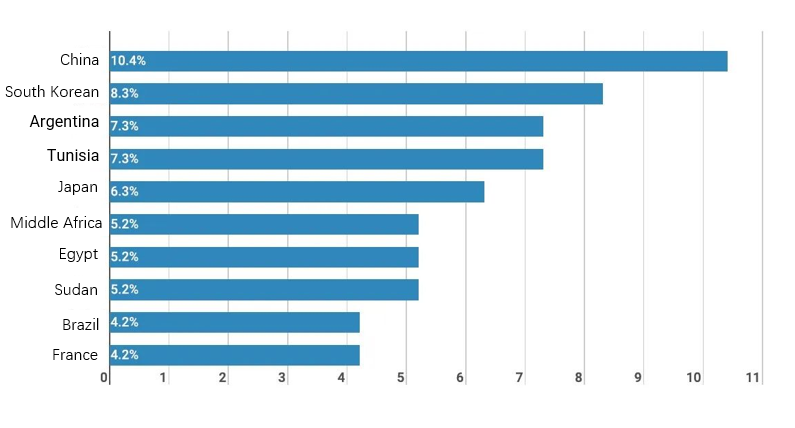
Figure 2. Top 10 countries with the number of ITU-T SG Vice-President positions
2. Participation as ITU-T WP chairman, vice-chairman and rapporteur
China holds the highest number of chair positions in the ITU-T WP, followed by South Korea and Japan. At the same time, China, Argentina and the United Kingdom are the first three countries for vice-chair positions held (by country of registration of entities holding leadership positions, Figure 3).
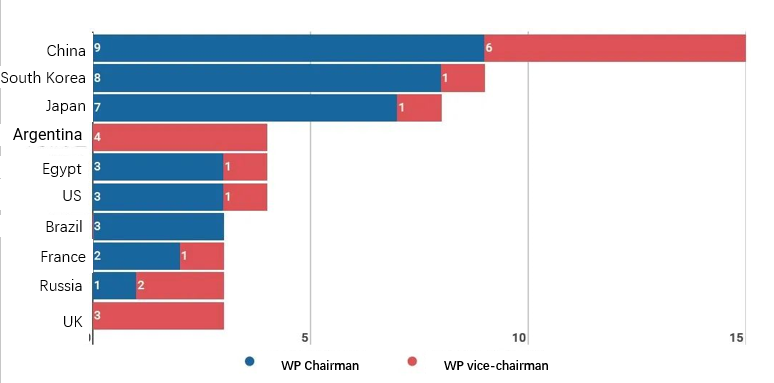
Figure 3 Distribution of ITU-T WP chair and vice chair positions by country of registration (top 10)
ITU-T has a total of 317 rapporteurs, of which 29% are represented by Chinese representatives, followed by peers from South Korea (13%), Japan (8%), the United States (5%) and Germany (4%). See Figure 4 for more details; while Figure 5 details the distribution of ITU-T rapporteurs among different entities.
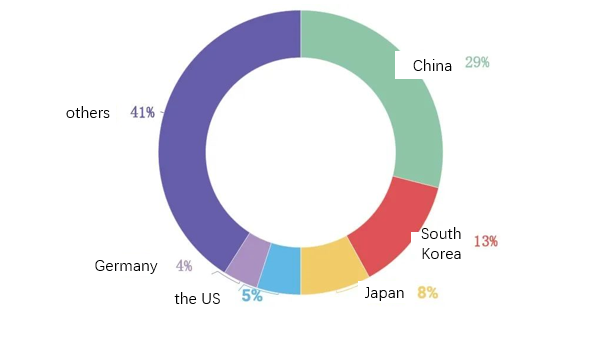
Figure 4. Distribution of ITU-T WG Rapporteur posts by country of entity registration
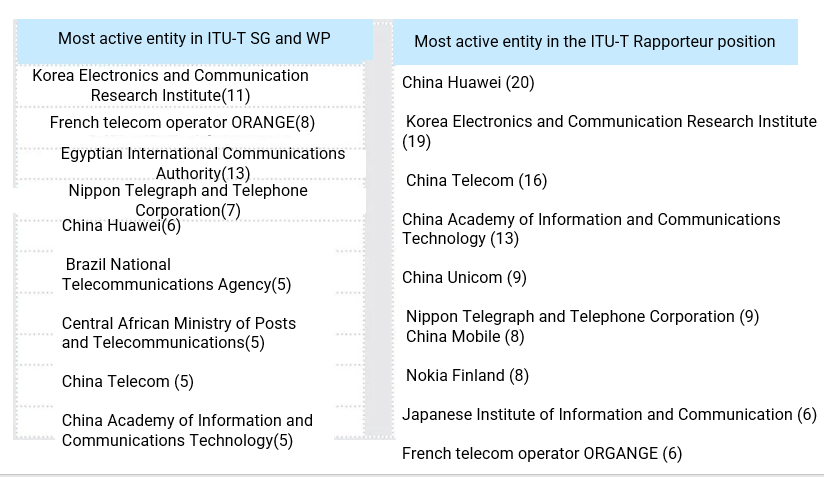
Figure 5. Activity of national entities in ITU-T
Comparing the national distribution of the roles of chair, vice-chair and rapporteur posts in ITU-T SG and WP between 2001-2004 and 2017-2020, it emerges how the influence of countries has changed significantly over the period.
Specifically, as illustrated in Figure 6, in the early 2000s, entities from the United States had the largest share: 22 chairs and vice-chairs (including SG and WP) and 60 rapporteurs. In contrast, back then China had a very limited number of representatives: 1 vice-chair and 3 rapporteurs.
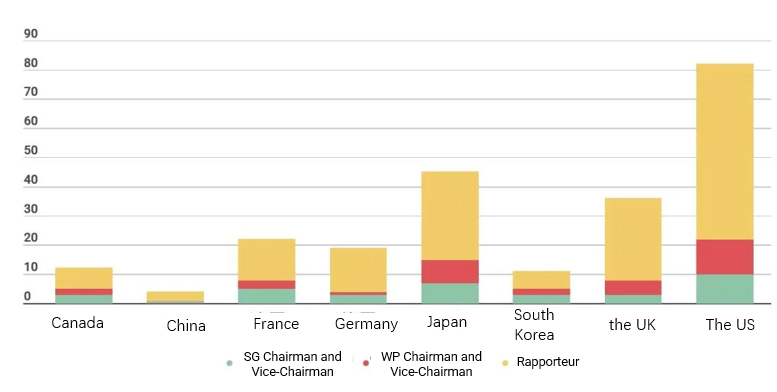
Figure 6 ITU-T various positions undertaken by countries in 2001-2004
However, as illustrated in Figure 7, the situation had changed drastically by 2021: entities from the United States had 5 chairs and vice-chairs, and 16 rapporteurs; while entities from China had 25 chairs and vice-chairs, and 89 rapporteurs.
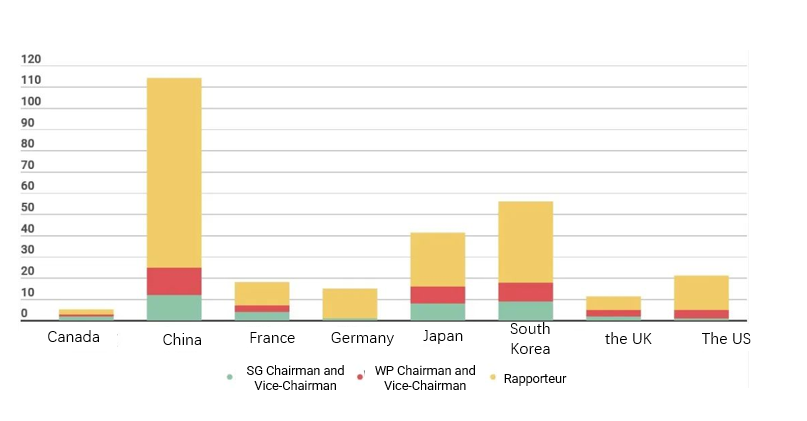
Figure 7. 2017-20020 ITU-T various positions undertaken by countries
Participation in ITU-R
1. Participation as Chairman and Vice-Chairman of ITU-R SG
ITU-R has six SGs, which are chaired by entities from Australia, Egypt, Japan, Russia, the UK and the US. China holds the same number of vice-chair positions as India and Morocco, followed by France, South Korea and Russia; while with the remaining 57 vice-chair positions are held by entities from other 37 countries (Figure 8).
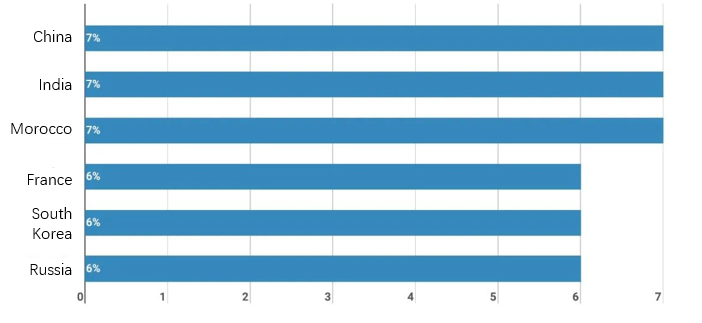
Figure 8. Top six countries as per ITU-R SG Vice-Chair positions held
2. Participation as ITU-R WP Chairman, Vice-Chairman and Rapporteur
The United States holds the largest number of ITU-R WP chair and vice chair positions, followed by China (by country of registration of entities holding leadership positions, Figure 9).
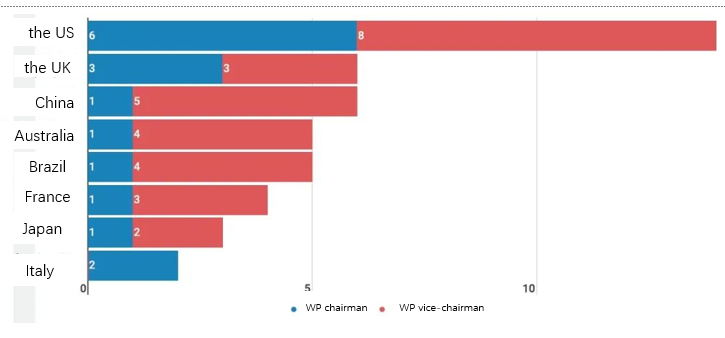
Figure 9 Distribution of ITU-R WP Chair and Vice-Chair positions by country of registration (top 8)
Source: Chinese Media




